【微雪 RP2040双核开发板】四 汉子字库 汉子显示
[复制链接]
资料:
一、Pycharm开发环境配置
1.安装micropython插件

2.关联pico

3.代码测试

二、汉子字库显示参考资料
下面分享前辈的设计理念即步骤教程。。
1.1.micropython 汉子开发 (字库版)
https://www.bilibili.com/video/av599593694/
1.2.micropython 字库生成
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1YD4y16739/?spm_id_from=333.788.video.desc.click
1.3.MicroPython 中文字库
https://github.com/AntonVanke/MicroPython-Chinese-Font
1.4.点阵字体自定义工具
2.ESP32 汉子显示 (取模版)
https://www.cnblogs.com/juwan/p/13198330.html
3.ssd1306OLED中文显示-MicroPython-ESP32-利用GB2312字库(非手动取模)
fb增强固件及字库.rar,这个很关键,正常的固件都不支持字库的方式显示字库。首先是没有字库对应的解析文件,就是根据汉子编码获取汉子的点阵信息。然后是microPython仅支持UTF-8
https://blog.csdn.net/hehedadaq/article/details/117596103
以上三种方式,第二种是最容易实现的,方法思路都很简单方便,第三种受固件限制,扩平台几乎不太可能,所以我最终使用的第一种通用的方式实现的。


- 实际效果如图所示,常用的3500个汉字以及英文字母和标点符号等都可以调用显示,字符的大小也可以切换。
1、大神写的实践步骤
# MicroPython-Chinese
MicroPython 的中文显示模块,使其可以在显示模块上显示汉字。此外也可以自定义字体集,使其能够满足不同存储空间、不同语言的要求。
### 资源
[MicroPython中文字库教程[BiliBili视频]](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV12B4y1B7Ff/)
[MicroPython 中文字库的使用演示文档](./doc/MicroPython%20中文字库的使用演示文档.md)
[如何生成点阵字体文件](https://github.com/AntonVanke/MicroPython_BitMap_Tools/blob/master/doc/如何生成点阵字体文件.md)
### 简单上手
所需
1. 运行 `micropython` 的开发板
2. 使用 `SSD1306 驱动芯片`的 `OLED 128*64` 屏幕
3. 拥有至少 `512Kbyte` 的空闲 ROM 空间和 `20 Kbyte`的空闲内存
**两步操作**
1. 将 `demo/ssd1306_demo.py`文件修改为你所连接的引脚
```python
i2c = I2C(scl=Pin(2), sda=Pin(3)) # line 16
```
2. 依次将`demo/ssd1306_demo.py`、`driver/ssd1306.py`、`ufont.py`、`unifont-14-12888-16.v3.bmf`上传到**开发板根目录**,运行`ssd1306_demo.py`即可
图片
如果你运行成功了,正常情况下是会显示
<img src="https://s1.ax1x.com/2022/07/31/vFBplT.jpg" alt="运行效果" style="zoom: 33%;" />
### 使用方法
**项目文件**
```shell
.
├── LICENSE
├── README.md
├── demo
│ ├── epaper1in54_demo.py # 1.54 英寸墨水屏例子
│ ├── ssd1306_demo.py # 0.96 英寸 OLED 例子
│ └── st7735_demo.py # 合宙 Air10x 系列屏幕扩展板驱动 例子(不完善)
├── doc
│ ├── MicroPython 中文字库的使用演示文档.md
│ └── 如何生成点阵字体文件.md
├── driver
│ ├── e1in54.py # 1.54 英寸墨水屏驱动
│ ├── ssd1306.py # 0.96 英寸 OLED 驱动
│ └── st7735.py # 合宙 Air10x 系列屏幕扩展板驱动
├── requirements.txt # python 库需求文件
├── ufont.py # ⭐库文件
└── unifont-14-12888-16.v3.bmf # ⭐生成的点阵字体
```
上传`ufont.py`、`unifont-14-12888-16.v3.bmf`到`MicroPython`根目录
**对于**`SSD1306(OLED 128*64)`
```python
from machine import Pin, I2C
import ssd1306
import ufont
i2c = I2C(scl=Pin(2), sda=Pin(3)) # 定义 I2C 管脚
display = ssd1306.SSD1306_I2C(128, 64, i2c) # 驱动对象
f = ufont.BMFont("unifont-14-12888-16.v3.bmf") # 中文显示对象
f.text(
display=display, # 显示对象 必要
string="", # 显示的文字 必要
x=0, # x 轴
y=0, # y 轴
color=1, # 颜色 默认是 1(黑白)
font_size=16, # 字号(像素)
reverse=False, # 逆置(墨水屏会用到)
clear=False, # 显示前清屏
show=False # 是否立即显示
)
```
**对于**`st7735(80*160)[合宙 Air10x 系列屏幕扩展板]`
详见[MicroPython 中文字库的使用演示文档](/doc/MicroPython%20中文字库的使用演示文档.md)
### 字体生成
#### 下载应用程序
[ufont 点阵字体生成工具](https://github.com/AntonVanke/MicroPython_BitMap_Tools/releases/tag/v0.0.1)
#### 详见
[如何生成点阵字体文件](https://github.com/AntonVanke/MicroPython_BitMap_Tools/blob/master/doc/如何生成点阵字体文件.md)
### 生成的字体文件格式
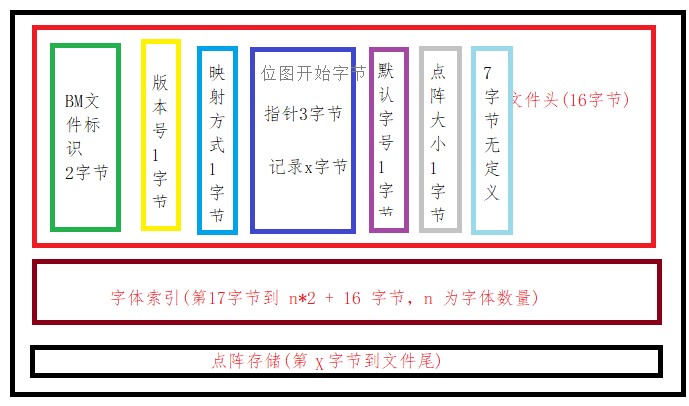
### 注意事项
1. 采用`Framebuf`缓冲区的驱动才能够使用
2. 最好全程使用推荐字号(16px)否则会有各种各样的问题
3. 主要缓冲区内存不足的问题(尤其是TFT屏幕)
- 实际区别
首先是芯片不同,固件不同,然后是显示屏的不同。相同的是字库文件相同,最后的实际字库代码略微调整。
所以在这个汉子的实践过程最主要的工作内容就是代码的移植。
3、准备文件
首先准备微雪的LCD显示列成代码(RP2040-LCD-1.28.py)和LCD用的固件(rp2-pico-20220117-v1.18.uf2),主要用做显示的驱动和主要函数代码。
然后准备使用的字库文件(unifont-14-12888-16.v3.bmf)和字库的解析程序(ufont),因为微雪官方提供的LCDDome是没有汉子显示的,其例程序可以画点、画线、字符显示等基础功能。
1.首先固件下载到pico当中,然后测试一下LCDDome工程。详细的操作可以查看此链接https://bbs.eeworld.com.cn/thread-1229748-1-1.html
2.将字库文件和字库解析文件下载到pico中,字库使用的是Unicode编码,并非GKB编码。如图所示:

3.代码功能块和作用
3.1代码内容的概述在代码程序中已备注的形式体现。当前状态程序内汉子字符不能直接转为Unicode的十六进制,目前也不在想继续开发这块代码,对于我这初学者来说进坑有点多有点耗时。
# encoding:utf-8
from machine import Pin,I2C,SPI,PWM,ADC
import framebuf
import time
import random
import ufont #字库解码程序文件调用
import binascii
I2C_SDA = 6 # I2C引脚声明 陀螺仪用
I2C_SDL = 7
DC = 8 # LCD引脚声明
CS = 9
SCK = 10
MOSI = 11
RST = 12
BL = 25 #LCD背光
Vbat_Pin = 29 #电池电压检测引脚
class LCD_1inch28(framebuf.FrameBuffer): #LCD初始化和子函数
def __init__(self):
self.width = 240
self.height = 240
self.cs = Pin(CS,Pin.OUT)
self.rst = Pin(RST,Pin.OUT)
self.cs(1)
self.spi = SPI(1,100_000_000,polarity=0, phase=0,sck=Pin(SCK),mosi=Pin(MOSI),miso=None)
self.dc = Pin(DC,Pin.OUT)
self.dc(1)
self.buffer = bytearray(self.height * self.width * 2)
super().__init__(self.buffer, self.width, self.height, framebuf.RGB565)
self.init_display()
self.red = 0x07E0
self.green = 0x001f
self.blue = 0xf800
self.white = 0xffff
self.colorData = bytearray(2)
self.windowLocData = bytearray(4)
self.fill(self.white)
self.show()
self.pwm = PWM(Pin(BL))
self.pwm.freq(1000)
def write_cmd(self, cmd):
self.cs(1)
self.dc(0)
self.cs(0)
self.spi.write(bytearray([cmd]))
self.cs(1)
def write_data(self, buf):
self.cs(1)
self.dc(1)
self.cs(0)
self.spi.write(bytearray([buf]))
self.cs(1)
def set_bl_pwm(self,duty):
self.pwm.duty_u16(duty)#max 65535
def init_display(self):
"""Initialize dispaly"""
self.rst(1)
time.sleep(0.01)
self.rst(0)
time.sleep(0.01)
self.rst(1)
time.sleep(0.05)
self.write_cmd(0xEF)
self.write_cmd(0xEB)
self.write_data(0x14)
self.write_cmd(0xFE)
self.write_cmd(0xEF)
self.write_cmd(0xEB)
self.write_data(0x14)
self.write_cmd(0x84)
self.write_data(0x40)
self.write_cmd(0x85)
self.write_data(0xFF)
self.write_cmd(0x86)
self.write_data(0xFF)
self.write_cmd(0x87)
self.write_data(0xFF)
self.write_cmd(0x88)
self.write_data(0x0A)
self.write_cmd(0x89)
self.write_data(0x21)
self.write_cmd(0x8A)
self.write_data(0x00)
self.write_cmd(0x8B)
self.write_data(0x80)
self.write_cmd(0x8C)
self.write_data(0x01)
self.write_cmd(0x8D)
self.write_data(0x01)
self.write_cmd(0x8E)
self.write_data(0xFF)
self.write_cmd(0x8F)
self.write_data(0xFF)
self.write_cmd(0xB6)
self.write_data(0x00)
self.write_data(0x20)
self.write_cmd(0x36)
self.write_data(0x98)
self.write_cmd(0x3A)
self.write_data(0x05)
self.write_cmd(0x90)
self.write_data(0x08)
self.write_data(0x08)
self.write_data(0x08)
self.write_data(0x08)
self.write_cmd(0xBD)
self.write_data(0x06)
self.write_cmd(0xBC)
self.write_data(0x00)
self.write_cmd(0xFF)
self.write_data(0x60)
self.write_data(0x01)
self.write_data(0x04)
self.write_cmd(0xC3)
self.write_data(0x13)
self.write_cmd(0xC4)
self.write_data(0x13)
self.write_cmd(0xC9)
self.write_data(0x22)
self.write_cmd(0xBE)
self.write_data(0x11)
self.write_cmd(0xE1)
self.write_data(0x10)
self.write_data(0x0E)
self.write_cmd(0xDF)
self.write_data(0x21)
self.write_data(0x0c)
self.write_data(0x02)
self.write_cmd(0xF0)
self.write_data(0x45)
self.write_data(0x09)
self.write_data(0x08)
self.write_data(0x08)
self.write_data(0x26)
self.write_data(0x2A)
self.write_cmd(0xF1)
self.write_data(0x43)
self.write_data(0x70)
self.write_data(0x72)
self.write_data(0x36)
self.write_data(0x37)
self.write_data(0x6F)
self.write_cmd(0xF2)
self.write_data(0x45)
self.write_data(0x09)
self.write_data(0x08)
self.write_data(0x08)
self.write_data(0x26)
self.write_data(0x2A)
self.write_cmd(0xF3)
self.write_data(0x43)
self.write_data(0x70)
self.write_data(0x72)
self.write_data(0x36)
self.write_data(0x37)
self.write_data(0x6F)
self.write_cmd(0xED)
self.write_data(0x1B)
self.write_data(0x0B)
self.write_cmd(0xAE)
self.write_data(0x77)
self.write_cmd(0xCD)
self.write_data(0x63)
self.write_cmd(0x70)
self.write_data(0x07)
self.write_data(0x07)
self.write_data(0x04)
self.write_data(0x0E)
self.write_data(0x0F)
self.write_data(0x09)
self.write_data(0x07)
self.write_data(0x08)
self.write_data(0x03)
self.write_cmd(0xE8)
self.write_data(0x34)
self.write_cmd(0x62)
self.write_data(0x18)
self.write_data(0x0D)
self.write_data(0x71)
self.write_data(0xED)
self.write_data(0x70)
self.write_data(0x70)
self.write_data(0x18)
self.write_data(0x0F)
self.write_data(0x71)
self.write_data(0xEF)
self.write_data(0x70)
self.write_data(0x70)
self.write_cmd(0x63)
self.write_data(0x18)
self.write_data(0x11)
self.write_data(0x71)
self.write_data(0xF1)
self.write_data(0x70)
self.write_data(0x70)
self.write_data(0x18)
self.write_data(0x13)
self.write_data(0x71)
self.write_data(0xF3)
self.write_data(0x70)
self.write_data(0x70)
self.write_cmd(0x64)
self.write_data(0x28)
self.write_data(0x29)
self.write_data(0xF1)
self.write_data(0x01)
self.write_data(0xF1)
self.write_data(0x00)
self.write_data(0x07)
self.write_cmd(0x66)
self.write_data(0x3C)
self.write_data(0x00)
self.write_data(0xCD)
self.write_data(0x67)
self.write_data(0x45)
self.write_data(0x45)
self.write_data(0x10)
self.write_data(0x00)
self.write_data(0x00)
self.write_data(0x00)
self.write_cmd(0x67)
self.write_data(0x00)
self.write_data(0x3C)
self.write_data(0x00)
self.write_data(0x00)
self.write_data(0x00)
self.write_data(0x01)
self.write_data(0x54)
self.write_data(0x10)
self.write_data(0x32)
self.write_data(0x98)
self.write_cmd(0x74)
self.write_data(0x10)
self.write_data(0x85)
self.write_data(0x80)
self.write_data(0x00)
self.write_data(0x00)
self.write_data(0x4E)
self.write_data(0x00)
self.write_cmd(0x98)
self.write_data(0x3e)
self.write_data(0x07)
self.write_cmd(0x35)
self.write_cmd(0x21)
self.write_cmd(0x11)
time.sleep(0.12)
self.write_cmd(0x29)
time.sleep(0.02)
self.write_cmd(0x21)
self.write_cmd(0x11)
self.write_cmd(0x29)
def show(self):
self.write_cmd(0x2A)
self.write_data(0x00)
self.write_data(0x00)
self.write_data(0x00)
self.write_data(0xef)
self.write_cmd(0x2B)
self.write_data(0x00)
self.write_data(0x00)
self.write_data(0x00)
self.write_data(0xEF)
self.write_cmd(0x2C)
self.cs(1)
self.dc(1)
self.cs(0)
self.spi.write(self.buffer)
self.cs(1)
def _writedata( self, aData ) :
'''Write given data to the device. This may be
either a single int or a bytearray of values.'''
self.cs(1)
self.dc(1)
self.cs(0)
self.spi.write(aData)
self.cs(1)
def _pushcolor( self, aColor ) :
self.colorData[0] = aColor >> 8
self.colorData[1] = aColor
self._writedata(self.colorData)
class QMI8658(object): #陀螺仪初始化 以及陀螺仪函数
def __init__(self,address=0X6B):
self._address = address
self._bus = I2C(id=1,scl=Pin(I2C_SDL),sda=Pin(I2C_SDA),freq=100_000)
bRet=self.WhoAmI()
if bRet :
self.Read_Revision()
else :
return 0
self.Config_apply()
def _read_byte(self,cmd):
rec=self._bus.readfrom_mem(int(self._address),int(cmd),1)
return rec[0]
def _read_block(self, reg, length=1):
rec=self._bus.readfrom_mem(int(self._address),int(reg),length)
return rec
def _read_u16(self,cmd):
LSB = self._bus.readfrom_mem(int(self._address),int(cmd),1)
MSB = self._bus.readfrom_mem(int(self._address),int(cmd)+1,1)
return (MSB[0] << 8) + LSB[0]
def _write_byte(self,cmd,val):
self._bus.writeto_mem(int(self._address),int(cmd),bytes([int(val)]))
def WhoAmI(self):
bRet=False
if (0x05) == self._read_byte(0x00):
bRet = True
return bRet
def Read_Revision(self):
return self._read_byte(0x01)
def Config_apply(self):
# REG CTRL1
self._write_byte(0x02,0x60)
# REG CTRL2 : QMI8658AccRange_8g and QMI8658AccOdr_1000Hz
self._write_byte(0x03,0x23)
# REG CTRL3 : QMI8658GyrRange_512dps and QMI8658GyrOdr_1000Hz
self._write_byte(0x04,0x53)
# REG CTRL4 : No
self._write_byte(0x05,0x00)
# REG CTRL5 : Enable Gyroscope And Accelerometer Low-Pass Filter
self._write_byte(0x06,0x11)
# REG CTRL6 : Disables Motion on Demand.
self._write_byte(0x07,0x00)
# REG CTRL7 : Enable Gyroscope And Accelerometer
self._write_byte(0x08,0x03)
def Read_Raw_XYZ(self):
xyz=[0,0,0,0,0,0]
raw_timestamp = self._read_block(0x30,3)
raw_acc_xyz=self._read_block(0x35,6)
raw_gyro_xyz=self._read_block(0x3b,6)
raw_xyz=self._read_block(0x35,12)
timestamp = (raw_timestamp[2]<<16)|(raw_timestamp[1]<<8)|(raw_timestamp[0])
for i in range(6):
# xyz=(raw_acc_xyz[(i*2)+1]<<8)|(raw_acc_xyz[i*2])
# xyz[i+3]=(raw_gyro_xyz[((i+3)*2)+1]<<8)|(raw_gyro_xyz[(i+3)*2])
xyz = (raw_xyz[(i*2)+1]<<8)|(raw_xyz[i*2])
if xyz >= 32767:
xyz = xyz-65535
return xyz
def Read_XYZ(self):
xyz=[0,0,0,0,0,0]
raw_xyz=self.Read_Raw_XYZ()
#QMI8658AccRange_8g
acc_lsb_div=(1<<12)
#QMI8658GyrRange_512dps
gyro_lsb_div = 64
for i in range(3):
xyz=raw_xyz/acc_lsb_div#(acc_lsb_div/1000.0)
xyz[i+3]=raw_xyz[i+3]*1.0/gyro_lsb_div
return xyz
def TFTColor( aR, aG, aB ) :
'''Create a 16 bit rgb value from the given R,G,B from 0-255.
This assumes rgb 565 layout and will be incorrect for bgr.'''
return ((aR & 0xF8) << 8) | ((aG & 0xFC) << 3) | (aB >> 3)
class utf8_gb2312(object): #utf-8 转 GB2312编码 在此没有用到
def __init__(self):
self.f = open('font.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8')
def b2i(self, byte): # bytes转int
r = 0
for i in range(len(byte)):
r = (r << 8) + byte
return r
def i2b(self, num): # int转bytes
num = int(num, 16)
return num.to_bytes(2, 'big')
def one_char(self, char): # 将一个字符转化成gb2312
utf_byte = char.encode('utf-8')
r = self.B_S(0, 7296, self.b2i(utf_byte))
gb2312_byte = self.i2b(r)
# print(gb2312_byte)
return gb2312_byte
def str(self, st): # 将字符串转化成gb2312
r = b''
for s in st:
# print(s.encode('utf-8'))
if len(s.encode('utf-8')) <= 1:
r += s.encode('utf-8')
else:
r += self.one_char(s)
return r
def B_S(self, low, high, m): # 二分查找
if 0 <= low <= high <= 7296:
mid = (low + high) // 2
self.f.seek(mid * 12)
data = self.f.read(12)
utf = data[0:6]
if int(utf, 16) < m:
return self.B_S(mid + 1, high, m)
elif int(utf, 16) > m:
return self.B_S(low, mid - 1, m)
else:
return data[7:-1]
def __del__(self):
self.f.close()
'''
if __name__ == '__main__':
font = utf8_gb2312()
r = font.one_char('中')
print(r)
print(r.decode('gb2312'))
r = font.str("起风了Abc123-")
print(r)
print(r.decode('gb2312'))
'''
if __name__=='__main__':
LCD = LCD_1inch28()#初始化LCD
LCD.set_bl_pwm(65535)#初始化背光
qmi8658=QMI8658()#初始化陀螺仪
Vbat= ADC(Pin(Vbat_Pin)) #初始化ADC电压采集
print(issubclass(LCD_1inch28, framebuf.FrameBuffer))
f = ufont.BMFont("unifont-14-12888-16.v3.bmf") # 加载字库 Unicode字库 不仅有汉子还有字符串
#f = ufont.BMFont("GB2312.DZK")
f.text(LCD,"0123456",0,80,120,LCD.white,font_size=16,reverse=True,show=True) #文字显示函数
'''
文字显示函数的内容介绍
display=display, # 显示对象 必要
string="", # 显示的文字字符串 必要
hz=, # 汉子显示 如果汉子显示 设置string为'?' 如果显示字符hz=0
x=0, # x 轴
y=0, # y 轴
color=1, # 颜色 默认是 1(黑白)
font_size=16, # 字号(像素)
reverse=False, # 逆置(墨水屏会用到)
clear=False, # 显示前清屏
show=False # 是否立即显示
'''
#取模方式显示汉子 start
pattern = [0x81,0x00,0x41,0x00,0x21,0x00,0x11,0x00,0x09,0x00,0x05,0x00,0x02,0x80,0x03,0x80,
0x04,0xC0,0x04,0x40,0x08,0x20,0x08,0x30,0x10,0x18,0x20,0x0C,0x40,0x06,0x80,0x03]
buf = framebuf.FrameBuffer(bytearray(pattern), 16, 16, framebuf.MONO_HLSB)
#LCD.blit(buf, 140, 140,LCD.white)
#取模方式显示汉子 end
while(True):
#read QMI8658
'''
隐藏部分为 微雪Dome列出内容
xyz=qmi8658.Read_XYZ()
LCD.fill(LCD.white)
LCD.fill_rect(0,0,240,40,LCD.red)
LCD.text("RP2040-LCD-1.28",60,25,LCD.white)
LCD.fill_rect(0,40,240,40,LCD.blue)
#LCD.text(display,"浣犲ソ寰�杞�闆呴粦",80,57,LCD.white)
LCD.fill_rect(0,80,120,120,0x1805)
LCD.text("ACC_X={:+.2f}".format(xyz[0]),20,100-3,LCD.white)
LCD.text("ACC_Y={:+.2f}".format(xyz[1]),20,140-3,LCD.white)
LCD.text("ACC_Z={:+.2f}".format(xyz[2]),20,180-3,LCD.white)
LCD.fill_rect(120,80,120,120,0xF073)
LCD.text("GYR_X={:+3.2f}".format(xyz[3]),125,100-3,LCD.white)
LCD.text("GYR_Y={:+3.2f}".format(xyz[4]),125,140-3,LCD.white)
LCD.text("GYR_Z={:+3.2f}".format(xyz[5]),125,180-3,LCD.white)
LCD.fill_rect(0,200,240,40,0x180f)
reading = Vbat.read_u16()*3.3/65535*2
LCD.text("Vbat={:.2f}".format(reading),80,215,LCD.white)
LCD.show()
#'''
# 循环内循环的扫描显示内容
f.text(LCD,"chinese",0,80,57,LCD.white,font_size=24,reverse=True,show=True)
#utf-8 转 GB2312编码 因为开始的时候以为使用的是GBk编码 在网上找到了此段代码
font = utf8_gb2312()
r = font.one_char('撑')
#print(r)
#utf-8 转 GB2312编码
#f.char(LCD,"我", reverse=True, color=0xffff, font_size=16)
#汉子显示初步完成
hzst = [0x6c49,0x5b50,0x663e,0x793a,0x521d,0x6b65,0x5b8c,0x6210]
#LCD显示 汉子显示目前是逐个字的显示,还有待优化
f.text(LCD,'?',hzst[0],20,90,LCD.white,font_size=16,reverse=True,show=True)
f.text(LCD,'?',hzst[1],40,90,LCD.white,font_size=16,reverse=True,show=True)
f.text(LCD,'?',hzst[2],60,90,LCD.white,font_size=16,reverse=True,show=True)
f.text(LCD,'?',hzst[3],80,90,LCD.white,font_size=16,reverse=True,show=True)
f.text(LCD,'?',hzst[4],100,90,LCD.white,font_size=16,reverse=True,show=True)
f.text(LCD,'?',hzst[5],120,90,LCD.white,font_size=16,reverse=True,show=True)
f.text(LCD,'?',hzst[6],140,90,LCD.white,font_size=16,reverse=True,show=True)
f.text(LCD,'?',hzst[7],160,90,LCD.white,font_size=16,reverse=True,show=True)
f.text(LCD,'?',hzst[0],20,150,LCD.white,font_size=24,reverse=True,show=True)
f.text(LCD,'?',hzst[1],44,150,LCD.white,font_size=24,reverse=True,show=True)
f.text(LCD,'?',hzst[2],68,150,LCD.white,font_size=24,reverse=True,show=True)
f.text(LCD,'?',hzst[3],92,150,LCD.white,font_size=24,reverse=True,show=True)
f.text(LCD,'?',hzst[4],116,150,LCD.white,font_size=24,reverse=True,show=True)
f.text(LCD,'?',hzst[5],120,150,LCD.white,font_size=24,reverse=True,show=True)
f.text(LCD,'?',hzst[6],144,150,LCD.white,font_size=24,reverse=True,show=True)
f.text(LCD,'?',hzst[7],168,150,LCD.white,font_size=24,reverse=True,show=True)
'''
隐藏代码为微雪Dome程序
RED = TFTColor(0xFF, 0x00, 0x00)
f=open('spaceman.bmp', 'rb')
if f.read(2) == b'BM': #header
print('Hello MicroPython.bmp')
dummy = f.read(8) #file size(4), creator bytes(4)
print('dummy',dummy)
offset = int.from_bytes(f.read(4), 'little')
print('offset',offset).
hdrsize = int.from_bytes(f.read(4), 'little')
print('hdrsize',hdrsize)
width = int.from_bytes(f.read(4), 'little')
height = int.from_bytes(f.read(4), 'little')
#RGB = bytearray(172800)
#RGB = f.read(57600)
#print('RGB',RGB)
if int.from_bytes(f.read(2), 'little') == 1: #planes must be 1
print('fsit MicroPython.bmp')
depth = int.from_bytes(f.read(2), 'little')
if depth == 24 and int.from_bytes(f.read(4), 'little') == 0:#compress method == uncompressed
print("Image size:", width, "x", height)
rowsize = (width * 3 + 3) & ~3
if height < 0:
height = -height
flip = False
else:
flip = True
w, h = width, height
for row in range(h):
if flip:
pos = offset + (height - 1 - row) * rowsize
else:
pos = offset + row * rowsize
if f.tell() != pos:
dummy = f.seek(pos)
for col in range(w):
bgr = bytearray(4)
bgr = f.read(3)
#print('bgr',bgr)
LCD._pushcolor(TFTColor(0xFF, 0x00, 0x00))
LCD.show()
'''
time.sleep(0.1) # 延时
3.2 .ufont.Py 部分内容说明,大神代码在文件前声明版本为Python __version__ = 3 但我的环境下运行的仍然是microPython V1.13 所以代码功能是有缺失的。
(1)word_code = ord(word) 将字符转换成十六进制,但是不能转换汉子。Python3 可以使用hz = hex(ord('中'))函数将汉子编码进行转换,但micropython不能直接转。
(2)如图所示此函数用于输入字符或汉子编码,根据输入得到点阵数据
(3)struct.unpack(">H", self.font.read(2))[0] 解包邴杜初字库内的十六进制点阵数据

- 其余功能在代码中有注释,详情查看代码
micropython编码
计划使用字库的方案做个汉子显示,如此可以兼容简体中文常用的3500多个汉子,要想使用此方案,就需要制作字库,需要转码,程序内的汉子字符需要转成十六进制用来调取字库内的点阵数据。
1.简述ASCII、Unicode、GBK、UTF-8编码的区别
ASCII:使用一个字节编码,所以它的范围基本是只有英文字母、数字和一些特殊符号 ,只有256个字符,使用8位二进制表示信息。
Unicode:使用32位表示信息,Unicode一般用于计算机内存中做计算。
GBK:只用来编码汉字的,GBK全称《汉字内码扩展规范》。使用双字节编码,一个中文占2个字节。
UTF-8:压缩Unicode,使用8位二进制表示信息,用尽量少的位数来表示信息,节省存储空间。UTF-8中一个中文占3个字节,UTF-8一般可用于网络传输和数据存储
- MicroPython
MicroPython个人用的也不是很多,对其不是完全的了解,在此阶段的开发学习中遇到了很多的困难。
- MicroPython是Python3编程语言的精简高效实现,包括Python标准款的一小部分,并且经过优化,可在微控制器和受限环境中运行。
- MicroPython的编码格式是UTF-8,不支持GBK等其他格式,Python3的编码格式是以Unicode为主并且支持utf-8的格式。Python3以下也需要注意。
- 下面是我测试的过程

如图所示:Thonny开发工具,运行的解释器是Raspberry Pi Pico

如图所示:thonny默认的解释器如图所示,即可以正确的执行,一个汉字两个字节,因为默认的解释器是Python3.版本

如图所示:PyCharm开发工具汉子转码为正确的,但是运行代码的是软件自带仿真,而不是实际的开发板上。此时的运行环境实际是Python3,多以转换是正确的的。
|  1/9
1/9 
 京公网安备 11010802033920号
Copyright © 2005-2025 EEWORLD.com.cn, Inc. All rights reserved
京公网安备 11010802033920号
Copyright © 2005-2025 EEWORLD.com.cn, Inc. All rights reserved






 提升卡
提升卡 变色卡
变色卡 千斤顶
千斤顶



